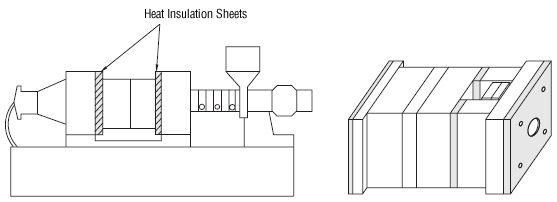
HEAT INSULATION SHEETS
Characteristics comparison of MISUMI insulation sheets

| Material grades | Standard | Heat proof | High strength | High temperature proof |
Bakelite (JIS PL-PEM) |
Bakelite (JIS PL-FLE) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Thickness high precision | Standard | Thickness high precision | |||||
| Standard type |
HIP | HIPH | HIPX | - | - | - | HIPP | HIPC |
| A/B dimension designation type |
HIPS | HIPHS | HIPXS | HIPXTS | HIPLS | HIPGTS | HIPPS | HIPCS |
| Bolt hole type |
HIPS-4H,6H | HIPHS-4H,6H | HIPXS-4H,6H | HIPXTS-4H,6H | HIPLS-4H,6H | HIPGTS-4H,6H | HIPPS-4H,6H | HIPCS-4H,6H |
| Boring type |
HIP-□□□□ | HIPH-□□□□ | HIPX-□□□□ | HIPXT-□□□□ | HIPL-□□□□ | HIPGT-□□□□ | HIPP-□□□□ | HIPC-□□□□ |
| Heat resistance | 5 | 9 | 4 | 9 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Insulation Efficiency |
5 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 8 | ||
| Bending strength |
5 | 3 | 10 | 6 | - | - | ||
| Compressive strength |
5 | 3 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 5 | ||
| Charpy impact value |
5 | 4 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Workability | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 9 | ||
| Cost benefit | 5 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 10 | 9 | ||
| Destruction temperature (note 1) |
400°C | 700°C | 300°C | 500°C | 180°C | 180°C | ||
| Recommended temperature (note 2) |
220°C or lower |
500°C or lower |
180°C or lower |
400°C or lower |
100°C or lower |
100°C or lower |
||
(note 2)"Recommended temperature"indicates temperature at which no sudden quality drop occurs when it is used for a long term.
Physical properties of the material
| Material grades | Standard | Heat proof | High strength | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items | Unit | HIP□ | HIPH□ | HIPX□ | ||
| General characteristics |
Specific gravity | - | 2.0~2.2 | 2.0~2.2 | 1.8 | |
| Water absorption | % | 2~5 | 4~6 | 0.03 | ||
| Electrical characteristics |
*Volume resistivity | Ω-cm | 4h/150°C | 2.0×1014 | 1.0×1012 | 2.0×1015 |
| 100h/ 25°C/ 90%RH |
3.0×109 | 1.0×107 | 1.0×1014 | |||
| Flatwise breakage voltage | kV/mm | 5~7 | 3 | 27 | ||
| Surface resistance | Ω | - | - | 2.0×1015 | ||
| Mechanical characteristics |
Bending strength | (SI unit)MPa | 98~147 | 44~54 | 400~500 | |
| kgf/cm2 | 1000~1500 | 450~550 | 4000~5000 | |||
| Compressive strength | (SI unit)MPa | 147~294 | 117~147 | 500~580 | ||
| kgf/cm2 | 1500~3000 | 1200~1500 | 5000~5800 | |||
| Charpy impact value |
(SI unit)J/cm2 | 1.4~1.5 | 1.0~1.1 | 9~10 | ||
| kgf·cm/cm2 | 14~15 | 10~11 | 90~100 | |||
| Thermal characteristics |
Expansion coefficient | I/°C | 6.6×10-6 | 9.0×10-6 | 1.6×10-4 | |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient |
(SI unit)W/m·K | 0.71 | 1.21 | 0.59 | ||
| cal/cm·sec·°C | 1.7×10-3 | 2.9×10-3 | 1.4×10-3 | |||
| kcal/h·m·°C | 0.61 | 1.04 | 0.50 | |||
| Specific heart | (SI unit)J/g·K | 1.08 | 0.92 | 1.15 | ||
| cal/g·°C | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.28 | |||
| Arc resistance | sec | 180 | 240 | 180 | ||
| Principal components |
Main binder | - | Inorganic material (Borate type binder) |
Inorganic material (Phosphatic type binder) |
Organic material (Super heat proof epoxy resin) |
|
| Base material | - | Glass fiber | Glass fiber | Glass fiber | ||
| Material grades | High temperature proof* | Bakelite (JIS PL-PEM) |
Bakelite (JIS PL-FLE) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items | Unit | HIPL□ | HIPG□ | HIPP□ | HIPC□ | ||
| General characteristics |
Specific gravity | - | 1.95~2.05 | 2.0~2.1 | 1.4 | 1.4 | |
| Water absorption | % | 0.05~0.06 | 0.1 | 0.5~0.6 | 0.9~1.4 | ||
| Electrical characteristics |
*Volume resistivity | Ω-cm | 4h/150°C | 5.7×1016 | 1.0×1015 | 3.0×109 | 4.0×108 |
| 100h/ 25°C/ 90%RH |
8.2×1015 | 1.0×1013 | 9.0×108 | 5.0×107 | |||
| Flatwise breakage voltage | kV/mm | 9~10 | - | 24~30 | 13~20 | ||
| Surface resistance | Ω | 3.0×1016 | - | 5.0×1010 | 9.0×108 | ||
| Mechanical characteristics |
Bending strength | (SI unit)MPa | 147 | 120~130 | - | - | |
| kgf/cm2 | 1400 ~ 1500 |
1200 ~ 1300 |
- | - | |||
| Compressive strength | (SI unit)MPa | 440~461 | 420~480 | 294~392 | 245~294 | ||
| kgf/cm2 | 4500 ~ 4700 |
4200 ~ 4800 |
3000 ~ 4000 |
2500 ~ 3000 |
|||
| Charpy impact value |
(SI unit)J/cm2 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 1.88 | 2.10 | ||
| kgf·cm/cm2 | 61.7 | 25.5 | 18.9 | 21.2 | |||
| Thermal characteristics |
Expansion coefficient | I/°C | 2.6×10-5 | 2.3×10-5 | 1.6×10-4 | 0.6×10-4 | |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient |
(SI unit)W/m·K | 0.24 | 0.3 | 0.21 | 0.38 | ||
| cal/cm·sec·°C | 0.58×10-3 | 0.7×10-3 | 0.5×10-3 | 0.9×10-3 | |||
| kcal/h·m·°C | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.32 | |||
| Specific heart | (SI unit)J/g·K | 0.99 | 0.90 | 1.60 | 1.30 | ||
| cal/g·°C | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.38 | 0.31 | |||
| Arc resistance | sec | 345 | - | - | - | ||
| Principal components |
Main binder | - | Inorganic material (Silica type binder) |
Inorganic material (Silica type binder) |
Organic material (Phenol resin) |
Organic material (Phenol resin) |
|
| Base material | - | Glass fiber | Glass fiber | Craft paper | Cotton cloth | ||
* Volume resistivity:top row values are measured after 4h/150°C, bottom row values under room temperature after 100h/25°C/90%RH.
* Upon use, make sure to check the temperature characteristics of mechanical strength(see the charts on)PDF (121KB)
* High temperature proof sheets include two products made by different manufacturers.
* For Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), please visit our homepage. (https://jp.misumi-ec.com/tech/msds/)
Method and Notes for machining Insulation sheet

 When machining, be sure to suck up dust into a dust collector so that it may not scatter. Safety measures for usual works in dust, such as masks and goggles, are required as the insulation sheets contain glass fiber which may affect the skin such as itching. When dust attaches to the machine, its accuracy may diminish.
When machining, be sure to suck up dust into a dust collector so that it may not scatter. Safety measures for usual works in dust, such as masks and goggles, are required as the insulation sheets contain glass fiber which may affect the skin such as itching. When dust attaches to the machine, its accuracy may diminish. Drilling holes in the insulation sheet may cause cracks. Attention needs to be taken to hole pitches, diameters, and etc.
Drilling holes in the insulation sheet may cause cracks. Attention needs to be taken to hole pitches, diameters, and etc.  These insulation sheets are lamination-formed products, and not suitable for tapping and 3-dimensional machining.
These insulation sheets are lamination-formed products, and not suitable for tapping and 3-dimensional machining.Machining Conditions
| Lathe turning | Milling | Drilling | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tools | Carbide (K-10) |
Carbide (K-10) |
Carbide (K-10) |
| Cutting speed V(m/min) |
Blade: Large~Small 45~200 |
Blade: Large~Small 100~300 |
Blade: Large~Small 120~350 |
| Revolution (rpm) |
Blade: Large~Small 50~1000 |
Blade: Large~Small 300~1000 |
φ2 gimlet 1000~1500 φ5 gimlet 500~1000 |
| Cutting depth (mm) |
0.5~0.3 | 0.5~2.0 | - |
| Feed (mm/revolution) |
0.1~0.2 | 0.1~0.2 | 0.1~0.5 |
 The above values are for reference only.
The above values are for reference only.
Note on handling
 The insulation sheet may break when the bolt is tightened too hard.
The insulation sheet may break when the bolt is tightened too hard. Do not use in areas where water, chemical or any liquids may come in. Insulation sheets that has absorbed water can be easily cracked, and cause significant degradation in their performance by increasing temperature.
Do not use in areas where water, chemical or any liquids may come in. Insulation sheets that has absorbed water can be easily cracked, and cause significant degradation in their performance by increasing temperature. When using the insulation sheets(Heat proof)at 300°Cor more, there may be some smoke or odor at first, but does not affect the product quality.
When using the insulation sheets(Heat proof)at 300°Cor more, there may be some smoke or odor at first, but does not affect the product quality. Refer to PDF (121KB) for property charts(durability data)on insulation sheets.
Refer to PDF (121KB) for property charts(durability data)on insulation sheets. Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) is published on our homepage.
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) is published on our homepage.(http://jp.misumi-ec.com/tech/msds/)
Example